- It is also called multi-tier architecture because the software is engineered to have the processing, data management, and presentation functions physically and logically separated.
- That means that these different functions are hosted on several machines or clusters, ensuring that services are provided without resources being shared and, as such, these services are delivered at top capacity.
- Not only does your software gain from being able to get services at the best possible rate, but it’s also easier to manage.
- This is because when you work on one section, the changes you make will not affect the other functions.
- This architecture would involve dividing an application into three different tiers: Logic Tier, Presentation Tier, Data Tier.
- The separate physical location of these tiers is what differentiates n-tier architecture from the MVC framework that only separates presentation, logic, and data tiers in concept.
- It also differs from MVC framework in that the former has a middle layer or a logic tier, which facilitates all communications between the different tiers.
- When you use the MVC framework, the interaction that happens is triangular; instead of going through the logic tier, it is the control layer that accesses the model and view layers, while the model layer accesses the view layer.
- Additionally, the control layer makes a model using the requirements and then pushes that model into the view layer.
- This is not to say that you can only use either the MVC framework or the n-tier architecture.
- You can use the n-tier architecture as the overall architecture, or use the MVC framework in the presentation tier.
Benefits
- Secure: You can secure each of the three tiers separately using different methods.
- You can store sensitive or confidential information in the logic tier, keeping it away from the presentation tier, thus making it more secure.
- Easy to manage: You can manage each tier separately, adding or modifying each tier without affecting the other tiers.
- Scalable: If you need to add more resources, you can do it per tier, without affecting the other tiers.
- Flexible: Apart from isolated scalability, you can also expand each tier in any manner that your requirements dictate.
- You can also adopt new technologies and add more components without having to rewrite the entire application or redesigning your whole software.
- More Efficient Development: N-tier architecture is very friendly for development, as different teams may work on each tier.
- This way, you can be sure the design and presentation professionals work on the presentation tier and the database experts work on the data tier.
- Easy to add new features: If you want to introduce a new feature, you can add it to the appropriate tier without affecting the other tiers.
- Easy to reuse. Because the application is divided into independent tiers, you can easily reuse each tier for other software projects.
- For instance, if you want to use the same program, but for a different data set, you can just replicate the logic and presentation tiers and then create a new data tier.
How It Works
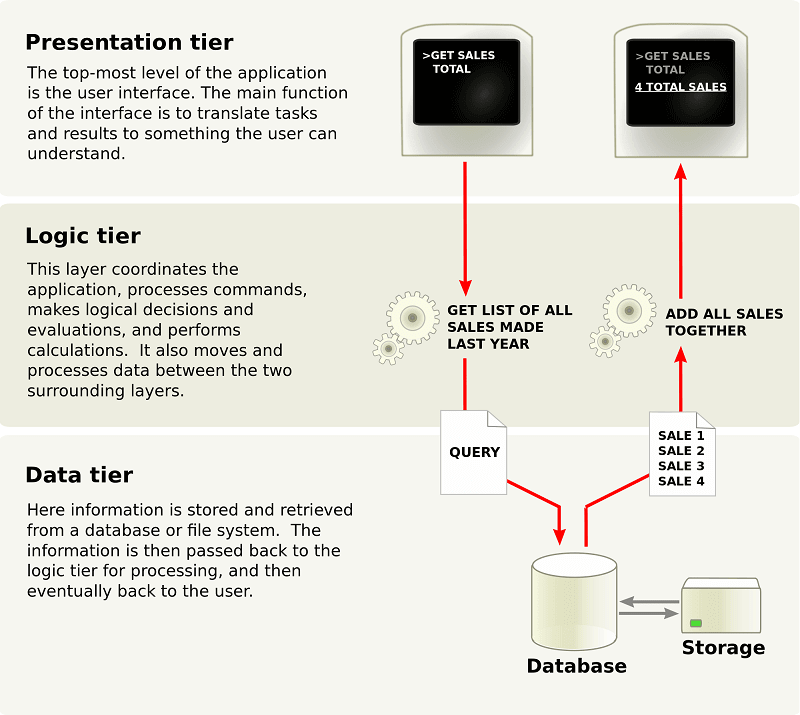
- The Application Logic tier. It is where all the “thinking” happens.
- It knows what is allowed by your application and what is possible, and it makes other decisions.
- This logic tier is also the one that writes and reads data into the data tier.
- The Data Tier. The data tier is where all the data used in your application are stored.
- You can securely store data on this tier, do transaction, and even search through volumes of data.
- The Presentation Tier. It is the user interface.
- This is what the software user sees and interacts with.
- This tier also acts as a go-between for the data tier and the user, passing on the user’s different actions to the logic tier.
- The presentation tier can be a Web application that you see.
- It is shown on a Web browser you access from your computer, and it has the CSS, JavaScript, and HTML codes that allow you to make sense of the Web application.
- The logic tier can be a .NET Web API, JSP, Java Servlets, Ruby, PHP and other technologies.
- The logic tier would be run on a Web server.
- The data tier would be some sort of database, such as a MySQL, NoSQL, or PostgreSQL database.
- There are n-tier architecture models that have more than three tiers:
- Services: such as print, directory, or database services
- Business domain: the tier that would host Java, DCOM, CORBA, and other application server object.

